CLOSE
About Elements
田中贵金属是贵金属领域的翘楚企业。
支撑社会发展的先进素材和解决方案、
创造了这些的开发故事、技术人员们的心声、以及经营理念和愿景——
Elements是以“探求贵金属的极致”为标语,
为促进实现更加美好的社会和富饶的地球未来传播洞察的网络媒体。

Royal Mint opens factory in south Wales to recover gold from e-waste
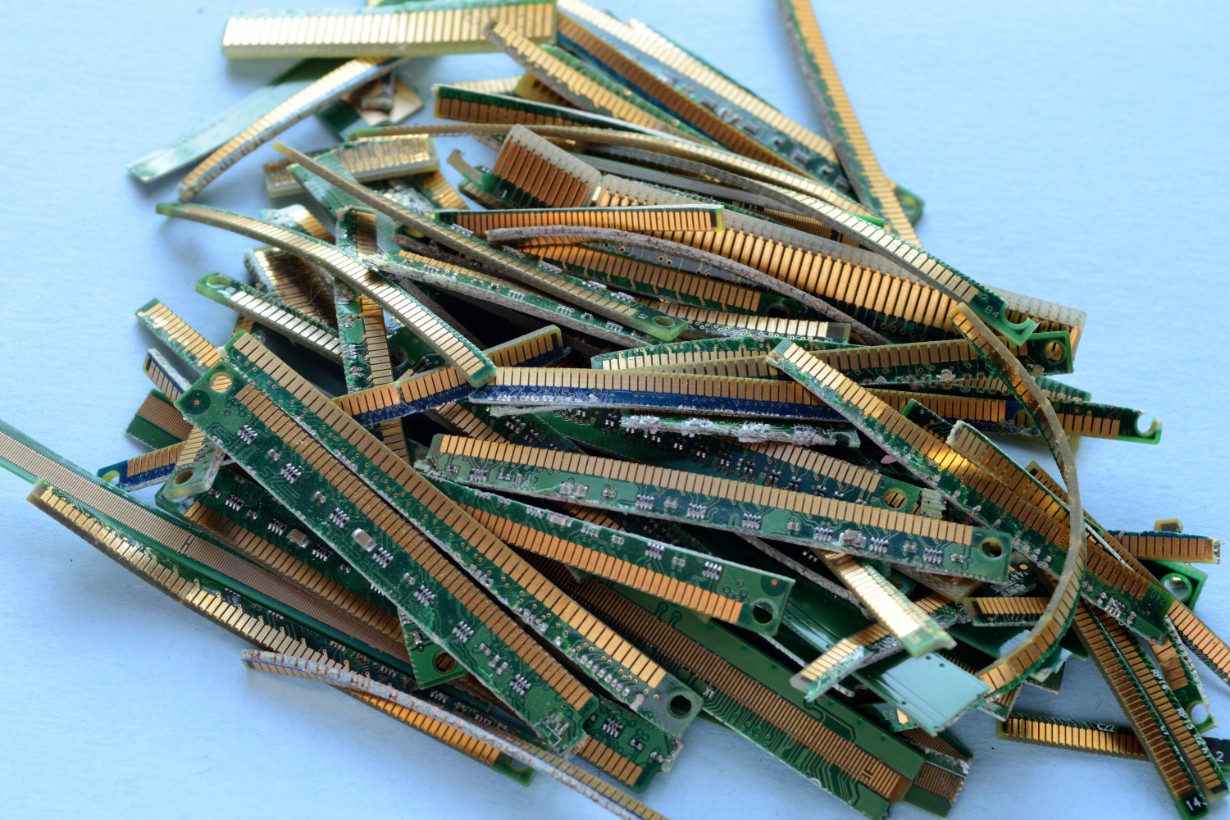
The Royal Mint has unveiled a “pioneering” factory that will recover gold from electronic waste, creating a more sustainable source of the precious metal for the coin manufacturer’s luxury jewellery line.
The factory in south Wales, which has been under construction since March 2022, is designed to extract gold from up to 4,000 tonnes a year of circuit boards sourced in the UK from electronics including phones, laptops and TVs.
The Royal Mint, which has produced coins for more than 1,100 years, has said the process could provide hundreds of kilograms of gold annually for its 886 jewellery range. This business, which launched in 2022, sells high-end rings, necklaces and earrings online and from its boutique in Burlington Arcade, in Mayfair, central London.
The gold will be extracted in two steps, with the Royal Mint processing the circuit boards in a specialised plant that separates the components and metals. The pieces containing gold will then be sent on to the south Wales factory.
The factory in Llantrisant will use patented new chemistry – created by the Canadian clean technology firm Excir – to recover the gold. A washing machine-style spinning drum washes the pieces of circuitry containing gold in a special acid mix that dissolves the precious metal in four minutes. That compares with other gold extraction processes that are more energy intensive and tend to require extremely high temperatures over a longer period of time.
It is estimated that about 600 mobile phones will have to be processed to create one of the 7.5g gold rings sold in the 886 collection, which are similar to the weight of a £1 coin.
The Mint said it expected to use the recovered gold in other parts of the business in the future, including for its commemorative coins.
The new factory is part of the Mint’s ongoing efforts to diversify its business as cash use continues to decline. The business is 100% owned by the UK Treasury and pays a dividend to the government each year, with remaining profits reinvested in the business.
“The Royal Mint is transforming for the future, and the opening of our precious metals recovery factory marks a pivotal step in our journey,” said the chief executive, Anne Jessopp.
This article was written by Kalyeena Makortoff from The Guardian and was legally licensed through the DiveMarketplace by Industry Dive. Please direct all licensing questions to legal@industrydive.com.
![]()







