CLOSE
About Elements
田中贵金属是贵金属领域的翘楚企业。
支撑社会发展的先进素材和解决方案、
创造了这些的开发故事、技术人员们的心声、以及经营理念和愿景——
Elements是以“探求贵金属的极致”为标语,
为促进实现更加美好的社会和富饶的地球未来传播洞察的网络媒体。

Opening the Way to the Future of Semiconductor Devices by Supplying State-of-the-Art Materials Made from Precious Metals
December 10, 2025 – Nikkei MOOK
Since it was founded in 1885, TANAKA has been active in a wide range of business fields centered on precious metals.
Roughly 70% of its business now consists of precious metal materials for industrial use, and it has a wide product lineup of semiconductor materials.
Let’s explore the initiatives TANAKA is carrying out in the field of power electronics.
The use of next-generation power semiconductors is rapidly growing more widespread
If logic semiconductors and memory semiconductors are the brains of electronic devices, then power semiconductors are their hearts. These components, which control and supply electrical power, are used in every kind of electronic device. They are critical components in electric vehicles (EVs), industrial equipment, telecommunications base stations, and the renewable energy field, which handle especially large amounts of power. The market for power semiconductors is expected to continue to grow in the future, and development of new technologies is accelerating with an eye towards reducing energy consumption.
The use of power semiconductors with wide band gaps is rising rapidly because so that the devices they are used in can operate stably even in harsh environments. Semiconductors made with silicon carbide (SiC) or gallium nitride (GaN) maintain greater stability and performance at high temperatures than conventional silicon semiconductors. Not only that, but they also excel at handling high power loads and high frequencies, so development work aimed at mass production is already underway.
However, as Yoshinori Fushimi of TANAKA PRECIOUS METAL TECHNOLOGIES Co., Ltd. explains, designers face new challenges when developing these next-generation power semiconductors. “The higher power levels involved raise the issues of how to deal with higher temperatures, how to maintain the reliability of connections when the components are undergoing thousands of heat cycles, and how to bond the large surface areas of larger chips (dies). These challenges are hard to meet with conventional solder paste or epoxy resin adhesive.”

Product Sales
Bonding Material Sales Section
Ag Adhesive Paste Product Manager

Product Sales
Bonding Material Sales Section
Ag Bonding Material Product Manager
Supplying materials to address these problems and enable free modular design
TANAKA supplies materials that solve these problems. One of these is Ag adhesive paste that changes how dies are bonded. The resin-enhanced silver sintering paste (commonly known as hybrid silver sintering paste) differs significantly from conventional silver sintering paste. “Not only does it excel at heat dissipation due to its high thermal conductivity,” says Fushimi, “but the unique resin system maintains a high level of reliability in the face of heat cycling, so it meets the needs of the harsh usage environments encountered when used in vehicles.” Fushimi is particularly proud of how well it performs with small and medium-sized dies, helping extend the lives of power devices and increase their capacities.
Another of these materials is the AgSnTLP sheet. These sheets are perfect for bonding large surfaces. Shinichiro Kitaoka, who was involved in the development process, explains, “These are Ag-Sn liquid phase diffusion bonding sheets that are effective when bonding large dies or modules.”
These sheets have three main features. The first is their reliability. After bonding, the silver (Ag) and tin (Sn) form Ag3Sn, so their heat resistance rises to 480°C. That gives them a higher level of heat resistance than conventional materials. The bonding strength can be as high as 50 MPa, and the sheets maintain the same bonding strength even at temperatures of 300°C. AgSnTLP sheets have passed heat cycle testing with 3,000 heat cycles. The second feature is their contribution to cost reductions. They bond in just minutes, so they lower process costs by reducing takt times. The third feature is their contribution to reducing environmental impacts. They contain no solvents, so they don’t produce any volatile organic compounds (VOCs). They also don’t contain any substances restricted by the RoHS Directive. “These sheets’ bonding process, which bonds securely with little pressure, along with their void reductions, streamlines manufacturing processes,” says Kitaoka. “They’re particularly well-suited for bonding the large surface areas of modules and heat sinks. We’re confident that they can improve heat dissipation.”
These two die bonding products, Ag adhesive paste and AgSnTLP sheets, are mutually complementary solutions. The features of each can be leveraged for different applications to produce true value. For example, Ag adhesive paste is suited for bonding small or medium dies, while AgSnTLP sheets are suited for bonding dies with large surface areas, where thermal stability is required. According to Kitaoka, “Using the two to supplement each other makes it possible to design modules more freely, something that is difficult with conventional products. They make simultaneous improvements to multiple critical aspects of next-generation power semiconductor development, such as thermal management, reliability, and manufacturability.”
Products offered by TANAKA, a total solution provider, for use in power devices
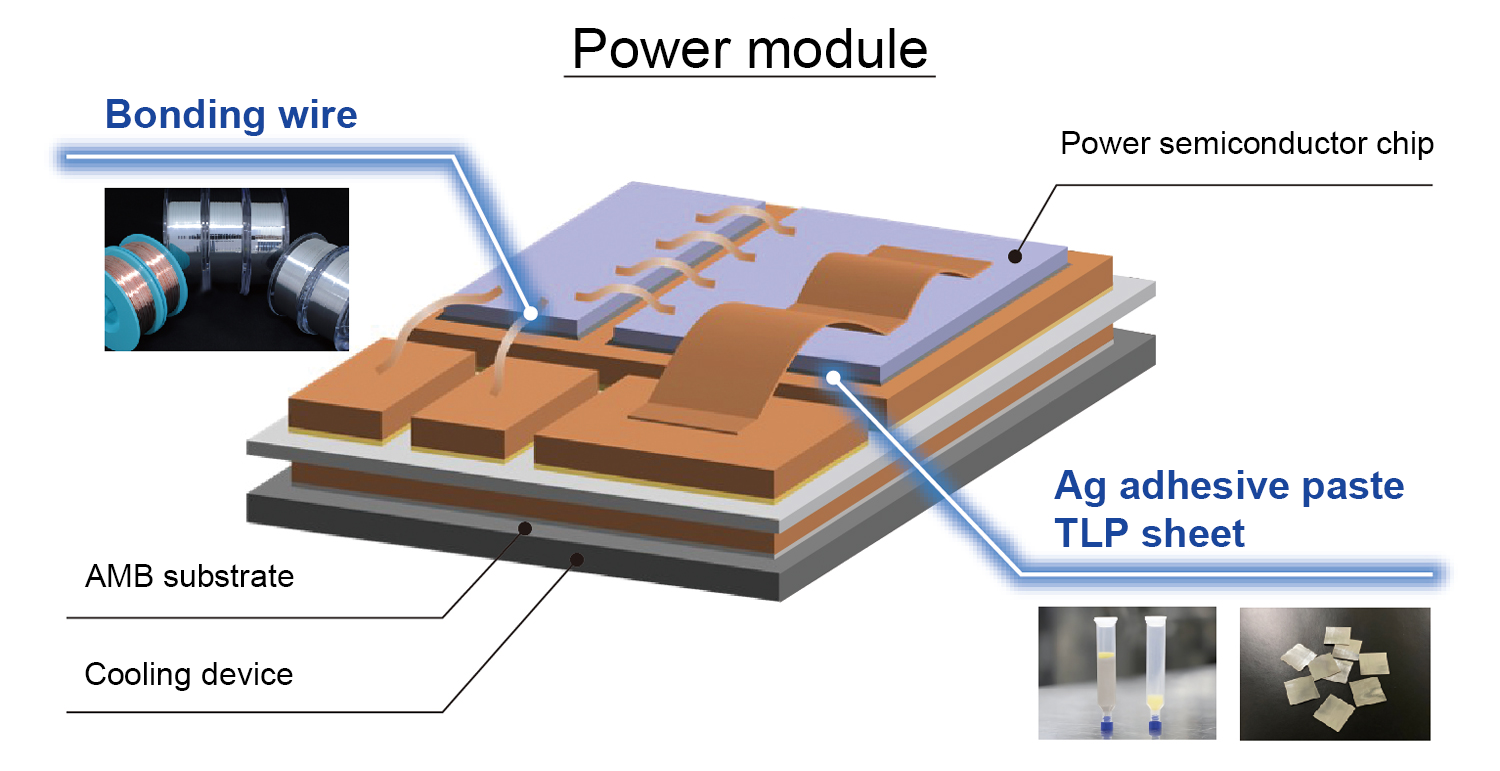
A full lineup of materials that covers everything from upstream to downstream
One of the critical requirements of power semiconductors is that they be able to control electricity even in relatively confined spaces, as epitomized by EVs. There is a growing need for power semiconductor materials that reduce resistance levels and deal with heat dissipation so that power semiconductors can maintain their high level of performance despite being more miniaturized.
TANAKA provides comprehensive solutions for products used with power devices. Not only does it supply die bonding materials, but it is also one of the world’s top suppliers of bonding wire, active brazing filler metals, plating processes, sputtering targets, and more. It maintains a steady supply of a full lineup of materials that covers everything from upstream to downstream manufacturing processes.
Also, the materials used are often rare, so TANAKA also takes into consideration the production and distribution systems used for precious metal materials, with an eye toward recycling. Precious metal recycling is one of TANAKA’s core businesses, and it has recycling sites worldwide.
As power semiconductors evolve, bonding material innovation is absolutely essential to deal with the issues of heat dissipation and reliability. TANAKA stands at the forefront of this innovation, poised to support the power electronics of the coming era.
It will continue to leverage the features of precious metals to research, develop, and supply state-of-the-art materials.
Related Information
Technology Trend and Advanced Packaging Material for Power Device
Power device is key component for a wide range of applications such as smartphones, electronic devices, next-generation mobility including EV and HEV, cellular base stations, power control for renewable energy and so on. Its technology development is thriving day by day.
We introduce advanced packaging technology trends and cutting-edge materials designed to address challenges such as high heat dissipation, high heat resistance, reliable bonding in manufacturing, and miniaturization.











